Imagine drifting off to sleep, wrapped in a cocoon of comfort, when suddenly you wake up gasping for air. This unsettling experience is known as Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND), and it can turn peaceful nights into distressing episodes. If you’ve ever found yourself struggling to catch your breath at night, you’re not alone. PND affects many individuals and can be linked to various underlying health issues.
Understanding PND is essential for anyone who has experienced this frightening phenomenon or cares for someone who has. What causes these nighttime breathlessness episodes? How does it relate to heart function? And what steps can be taken to manage or treat the condition effectively?
Join us as we explore the intricacies of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea, from its symptoms and triggers to diagnosis and treatment options. Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to our health, so let’s delve deeper into this often-overlooked topic and empower ourselves with the facts about nighttime breathlessness!
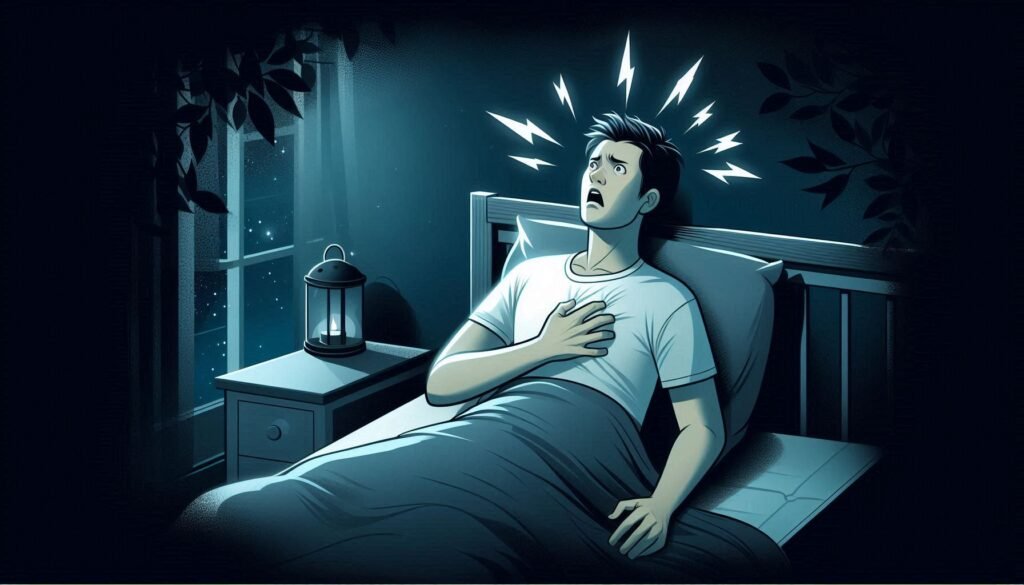

What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea? A Simple Explanation
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) is a sudden episode of severe breathlessness that occurs during sleep. This condition can jolt individuals awake, leaving them gasping for air and often feeling anxious.
Typically, PND happens after lying down for a period of time. The body struggles to maintain proper oxygen levels while in this position. Many people find relief by sitting up or standing, which allows gravity to help ease their breathing difficulties.
“What Causes Sudden Dyspnea? Understanding Breathing Difficulties”
This respiratory challenge is more than just an annoyance; it’s often linked to underlying health issues such as heart failure or pulmonary diseases. Recognizing PND early on can aid in effective management and treatment of these conditions, making awareness crucial for those at risk.
The Heart-Breath Connection: PND and Heart Failure
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) often signals an underlying heart issue, particularly heart failure. When the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently, fluid can accumulate in the lungs. This buildup leads to difficulty breathing at night.
As you lie down to sleep, gravity shifts body fluids. The increased pressure on lung tissues causes breathlessness. Many individuals with PND find themselves waking suddenly gasping for air.
“Why Is My Breathing So Fast? Understanding Tachypnea”
Heart failure isn’t just about fatigue or swelling of the legs; it can manifest dramatically during sleep. Recognizing this connection is vital for early intervention and management.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions can significantly alleviate PND symptoms. Addressing both cardiac health and respiratory function is essential for better quality of life in affected individuals.
Recognizing the Signs: Key Symptoms of PND
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) manifests through distinct symptoms that can be alarming. One of the most noticeable signs is sudden breathlessness during sleep, often waking individuals in a panicked state.
“What Are the Dangers of Hypoxemia? Signs You Need Medical Help”
This sensation may come with feelings of tightness in the chest. It’s not uncommon for patients to experience anxiety as they struggle to catch their breath.
In addition to shortness of breath, many report coughing or wheezing episodes at night. These respiratory challenges tend to worsen when lying flat.
As PND progresses, fatigue becomes more prevalent due to disrupted sleep patterns. Individuals may find it difficult to maintain energy levels throughout the day.
“How Do Chest Wall Disorders Impact Breathing? Complete Guide”
Awareness of these symptoms is crucial for early identification and intervention. Recognizing them can lead to timely medical advice and appropriate management strategies.
Nighttime Nemesis: Why PND Strikes During Sleep
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) often strikes when we are most vulnerable—during sleep. This sudden breathlessness can be alarming and disorienting.
The primary reason for this nighttime phenomenon lies in body position. When lying flat, fluid from the lower extremities redistributes into the bloodstream. As a result, it may accumulate in the lungs, leading to increased pressure and difficulty breathing.
“What Causes Altitude Sickness? Prevention & Treatment Guide”
Additionally, during deep sleep stages, our respiratory drive diminishes. This means our bodies may not respond as quickly to low oxygen levels or high carbon dioxide levels—a recipe for discomfort.
For those with underlying heart issues or pulmonary conditions, these factors exacerbate PND episodes. It’s crucial to understand why this occurs so patients can seek appropriate care and strategies to mitigate its effects during restful hours.
Common Causes: Understanding What Triggers PND
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) can be triggered by several underlying conditions. Heart failure is a primary culprit, as fluid accumulates in the lungs during sleep, making it harder to breathe.
“Is Epiglottitis Affecting Your Breathing? Emergency Warning Signs”
Obstructive sleep apnea also plays a significant role. This condition causes repeated interruptions in breathing throughout the night, leading to episodes of breathlessness.
Certain chronic lung diseases like COPD or asthma can exacerbate PND symptoms. These respiratory issues often worsen at night due to changes in air pressure and relaxation of airway muscles.
Additionally, high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems may increase the risk of developing PND. Fluctuations in body fluids during nighttime can intensify discomfort for those already predisposed.
“What Makes Pulmonary Edema Life-Threatening? Critical Signs”
Lifestyle factors such as obesity or excessive alcohol consumption contribute significantly to triggering episodes of PND. Addressing these triggers is vital for effective management and relief from this distressing condition.
Risk Factors: Who’s Most Likely to Experience PND?
Certain individuals are more prone to experiencing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). Understanding these risk factors can be crucial for early intervention.
Age is a significant factor. Older adults often face an increased likelihood of PND due to age-related changes in heart function and lung capacity.
“How Does Emphysema Progress? Understanding Lung Damage”
Additionally, those with pre-existing heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure or coronary artery disease, are at higher risk. These conditions can disrupt normal fluid balance and lead to breathing difficulties during sleep.
Obesity plays a role too. Excess weight can pressure the lungs and diaphragm, making it harder to breathe while lying down.
Lifestyle choices like smoking or having a sedentary routine contribute significantly. Both factors impact overall respiratory health and increase the chances of developing PND symptoms over time.
Diagnosis Journey: How Doctors Identify PND
Diagnosing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) involves a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. The journey often begins with a detailed patient history. Doctors will ask about the frequency and severity of breathlessness episodes, particularly during sleep.
Physical examinations play a crucial role as well. Physicians assess vital signs and listen to heart and lung sounds for any irregularities that might indicate underlying conditions.
Diagnostic tests are essential in confirming PND. Chest X-rays can reveal fluid accumulation or other abnormalities related to heart failure. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to rule out respiratory issues.
Sleep studies, or polysomnography, provide valuable insights into nighttime breathing patterns. These comprehensive evaluations help doctors pinpoint not just PND but any coexisting sleep disorders that could complicate treatment plans.
“What Makes Croup Different from Regular Coughs? Parent’s Guide”
Collaboration between specialists like cardiologists and pulmonologists is often key in this diagnostic process, ensuring all angles are considered for accurate identification.
The Sleep Study: Its Role in Diagnosing PND
The sleep study, also known as polysomnography, plays a crucial role in diagnosing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). This comprehensive test monitors various body functions during sleep. It tracks breathing patterns, heart rate, and oxygen levels.
During the study, patients spend the night in a specialized lab or at home with portable equipment. Electrodes are placed on the scalp and body to gather data while you sleep. This information helps doctors understand how your breathing changes throughout the night.
By analyzing these results, healthcare professionals can distinguish PND from other sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea. The detailed insights gained from a sleep study provide essential clues for effective treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Treatment Talk: Managing PND Effectively
Managing paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) effectively involves a multifaceted approach. Patients often benefit from lifestyle modifications, including weight management and regular exercise. These changes can alleviate strain on the heart and improve overall lung function.
“Why Does Central Sleep Apnea Happen? Understanding Brain Signals”
Medications play a crucial role in treatment as well. Diuretics help reduce excess fluid accumulation, which can lessen breathlessness during the night. ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers may also be prescribed to support heart health.
In some cases, supplemental oxygen therapy is recommended for those experiencing severe episodes of PND. This assists in maintaining adequate oxygen levels while sleeping.
Additionally, creating an optimal sleep environment is essential. Elevating the head with pillows or using specialized adjustable beds can significantly decrease nighttime symptoms by enhancing breathing mechanics during rest.
“What is Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis? Complete Guide”
Patient education about recognizing early signs of PND is vital for prompt intervention and effective management strategies.
Medications Matter: Drugs That Help Control PND
Medications play a crucial role in managing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). They aim to alleviate symptoms and improve overall nighttime breathing.
Diuretics are commonly prescribed for patients with heart failure. These drugs help reduce fluid buildup, easing pressure on the lungs. By removing excess fluid, they can significantly lessen breathlessness during sleep.
ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers also contribute effectively. These medications support heart function by lowering blood pressure and reducing strain on the heart. This can lead to better oxygenation during restful periods.
“How Does COPD Affect Daily Life? Management & Treatment”
In some cases, doctors may recommend bronchodilators. These assist in opening airways, making it easier to breathe at night.
It’s essential for patients to discuss their specific condition with healthcare providers. Personalized medication plans can make all the difference in controlling PND symptoms while promoting a more restful sleep experience.
Lifestyle Changes: Supporting Better Sleep with PND
Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly improve sleep quality for those experiencing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). First, establishing a consistent bedtime routine helps signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
Creating a calming sleep environment is crucial as well. Keep the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool to promote better rest. Consider using blackout curtains and white noise machines if necessary.
“What Are the Warning Signs of Pulmonary Embolism? Emergency Guide”
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can also be beneficial. Focus on whole foods rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime.
Regular physical activity plays an important role too. Engaging in light exercise during the day not only boosts cardiovascular health but also aids relaxation at night.
Managing stress through mindfulness techniques like meditation or yoga can help calm both mind and body before sleep. This holistic approach supports overall well-being while addressing PND symptoms effectively.
Position Matters: How Sleeping Posture Affects PND
The position in which you sleep can significantly influence Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). For many individuals, lying flat on their back may exacerbate breathlessness during the night.
This occurs because gravity causes fluid to redistribute in the body. When supine, fluids can accumulate in the lungs, making breathing more difficult. As a result, many people experience sudden awakenings due to shortness of breath.
Sleeping on your side might offer some relief. This position helps prevent fluid from pooling around the lungs and promotes better airflow. Using extra pillows or a wedge pillow can also elevate your upper body for added comfort.
Experimenting with different sleeping positions is crucial for managing PND symptoms effectively. A small adjustment could lead to significant improvements in your nighttime breathing patterns and overall restfulness.
PND vs. Sleep Apnea: Understanding the Differences
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) and sleep apnea are often confused due to their nighttime breathing issues. However, they have distinct characteristics.
PND typically occurs in individuals with heart failure or other cardiac conditions. It manifests as sudden episodes of breathlessness during sleep, waking the individual from rest. The sensation is usually temporary but can be distressing.
On the other hand, sleep apnea involves repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep caused by obstructed airways or central nervous system issues. This condition leads to snoring and gasping for breath, affecting overall sleep quality.
While both conditions disrupt restful nights, PND primarily indicates underlying heart problems. Sleep apnea may result from lifestyle factors like obesity or anatomical anomalies in the throat.
Understanding these differences is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment plans tailored to each condition’s unique challenges.
The Fluid Factor: How Body Fluid Shifts Affect PND
Fluid shifts in the body can significantly impact Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). During the day, gravity helps keep excess fluid in the lower extremities. However, when lying down at night, this fluid returns to circulation.
As fluids shift back into the bloodstream while you sleep, they may accumulate in the lungs. This accumulation leads to a sensation of breathlessness and discomfort. The heart struggles more under these conditions if there’s existing heart failure or compromised function.
Understanding this relationship between fluid dynamics and PND is crucial for effective management. Patients often find relief through diuretics that help reduce excess fluid buildup. Staying mindful of hydration levels during the day can also play a role in minimizing nighttime symptoms associated with PND.
Anxiety and PND: Breaking the Breathless Cycle
Anxiety often exacerbates the symptoms of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND). When individuals feel anxious, their body enters a heightened state of alertness. This can lead to rapid breathing and increased heart rate, intensifying feelings of breathlessness during the night.
When nighttime arrives, anxiety may spike as thoughts swirl around health concerns or fears related to PND. The link between mind and body is undeniable; stress can trigger episodes or make existing symptoms worse.
To break this cycle, relaxation techniques play a crucial role. Deep breathing exercises help calm the nervous system and lower anxiety levels. Mindfulness practices like meditation can also create a sense of peace before bed.
Creating a calming bedtime routine further supports mental health. A serene environment fosters better sleep quality and reduces nighttime panic associated with breathlessness.
Living with PND: Coping Strategies for Patients
Living with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) can be challenging, but there are effective coping strategies. Start by establishing a consistent nighttime routine. This helps signal your body that it’s time to relax.
Consider keeping a journal to track symptoms and triggers. Understanding patterns can empower you when discussing concerns with your doctor.
Breathing exercises can also play a significant role in managing episodes of breathlessness. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing may help reduce anxiety during the night.
Creating a sleep-friendly environment is essential too. Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet to promote better rest.
Don’t hesitate to lean on support networks—friends or online communities can provide encouragement and shared experiences that make living with PND more manageable.
Home Modifications: Creating a PND-Friendly Bedroom
Creating a PND-friendly bedroom involves thoughtful modifications that enhance comfort and accessibility. Start by ensuring good air circulation. A fan or an air purifier can help maintain fresh airflow, which may alleviate breathlessness.
Consider your mattress and pillows as well. Opt for adjustable models that allow you to elevate your upper body slightly while sleeping. This position can reduce pressure on the lungs, promoting easier breathing during the night.
Lighting also plays a crucial role in a restful environment. Use soft lighting to create a calming atmosphere, making it easier to relax without added stress.
Declutter your space. A tidy bedroom reduces anxiety and creates a peaceful setting conducive to sleep. These simple changes not only improve comfort but could significantly impact overall well-being for those dealing with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND).
When to Worry: Red Flags That Require Immediate Attention
Recognizing when to seek immediate care for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) is crucial. Certain symptoms signal a more serious issue that needs prompt attention.
If you experience severe breathlessness that doesn’t improve with sitting up or using prescribed medications, don’t hesitate to call for help. This could indicate worsening heart failure or another underlying condition.
Chest pain accompanying your PND should also raise alarms. It might be a sign of angina or even a heart attack, both requiring urgent evaluation.
Increased swelling in your legs or abdomen can suggest fluid buildup and may necessitate immediate medical intervention.
If you notice confusion or extreme fatigue alongside your breathing difficulties, these are additional red flags signaling that something isn’t right and requires swift action from healthcare professionals.
Long-term Outlook: What to Expect with PND
Living with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) can be challenging. Understanding the long-term outlook is crucial for both patients and caregivers.
Many individuals find that with proper management, episodes of PND become less frequent or severe. Effective treatment plans often lead to improved quality of life.
However, it’s essential to recognize that underlying conditions like heart failure may affect long-term outcomes. Regular medical check-ups help monitor these issues closely.
Patients are encouraged to remain proactive about their health. Lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy weight and managing stress levels, can have a significant impact on symptoms over time.
Engaging in open discussions with healthcare providers allows individuals to stay informed about advancements in treatments and strategies tailored specifically for them. Staying connected with support groups also fosters resilience throughout this journey.
Research Roundup: New Approaches to PND Management
Research into Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) continues to evolve, offering hope for those affected by this challenging condition. Recent studies are focusing on new treatment protocols and innovative management strategies that could significantly improve quality of life.
One promising area of research involves the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. While traditionally associated with sleep apnea, evidence suggests CPAP can also alleviate PND symptoms in certain patients. By maintaining open airways during sleep, it may help prevent the breathlessness that occurs at night.
Additionally, advancements in heart failure therapies are being explored as potential solutions for PND sufferers. Medications such as sacubitril-valsartan have shown promise in improving cardiac function and reducing fluid buildup—two significant contributors to nighttime breathing difficulties.
Another intriguing direction is the study of telemedicine and wearable technologies. These tools enable real-time monitoring of respiratory patterns and vital signs while allowing healthcare providers to adjust treatments promptly based on individual needs.
As researchers continue to delve deeper into understanding PND’s mechanisms, they aim to identify specific biomarkers that correlate with symptom severity. Such developments could lead to personalized medicine approaches tailored specifically for each patient’s profile.
Embracing a multidisciplinary approach—including cardiology, pulmonology, and even psychology—may yield comprehensive care models that address both physical symptoms and psychological factors like anxiety that often accompany PND.
With ongoing investigations shedding light on effective management options, individuals experiencing Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea can remain hopeful about future advancements aimed at enhancing their overall well-being.